从dva-loading源码了解dva插件式开发
2023-10-27
4426
什么是dva-loading
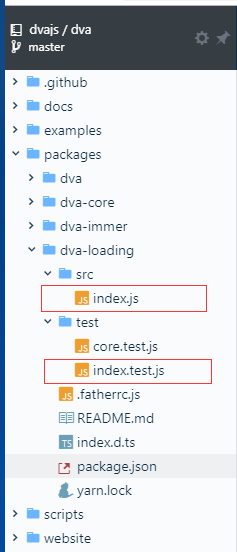
dva-loading是dva中的一个插件,由dva自带,主要是用状态表示effects里的某个generator是否在执行,探究一下dva-loading的实现,和插件化的加载方式。generator就是我们常写的 *开头的函数
代码入口
1.方法体
1 | |
2.方法体内的变量定义 和前置判断
1 | |
only是允许的actionexcept是排除的action两者只需用一个就行了SHOW和HIDE分别是两个type来控制loading的状态initialState里的models用key value形式来存命名空间和是否正在执行initialState里的effects用key value形式来存dispatch的type名和是否正在执行initialState里的global表示所有模块有没有正在执行的generator
3.reducer
1 | |
4.generator执行的监听
1 | |
5.返回结果
1 | |
use是如何使用
1 | |
结语
钩子如何调用还需再深入探究,就放到下一篇里探讨,文章写的比较简单,如果有谬误,欢迎指正。

查看评论